A string of natural or artificial fibres or filaments is called textile yarn. A fibre is a very short hair. A filament is a prolonged strand made of just one material. Individual strands or filaments are wrapped together to form threads in textile yarn.
Natural fibres from sources like wool from sheep, silk from silkworms, or cotton and linen from plants can be used to make textile yarn. Additionally, synthetic, or man-made fibres are derived from a number of materials, such as nylon, acrylic, and polyester.
There are two broad categories in which yarns can be categorised:
1. Spun or staple yarn
2. Filament yarn
Spun Yarn

Staple fibres are twisted together to form a strong thread called spun yarn. Spun yarns can be made from a single type of fibre or from a combination of different types.
Spun yarns can be further classified according to the number of yarns, type and degree of twist, spinning process used.
Filament Yarn

This yarn’s filaments are neatly aligned with the yarn axis and lie straight and parallel to it. As a result, filament yarns are often surface-smooth and densely packed.
Filament yarn can be of two types- mono and multifilament yarns which are further categorised as Twisted filament yarn, Rotto filament yarn, Zero twist filament yarn.
Novelty yarn

Novelty yarns are made up of mostly two or more stands. Produced for decorative surface effects, each strand is referred to as the base/core, effect, or binder depending on its intended use. Structure and strength are provided by the base/core strand. The effect strand makes ornamental details like loops and knots. If binding is required, the binder is used to connect the effect yarn to the base yarn.
Slub yarn:
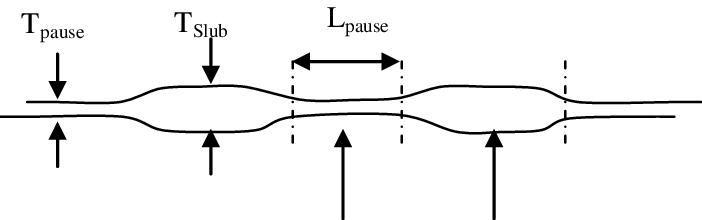
This yarn is used to give the fabric an organic, tactile look and feel that alternates thick and thin parts in a regular or irregular pattern.It can be either single-ply or multi-plys yarn.
Flock/flake yarn:
Flock/flake yarn is described as having little tufts of fibres in various colours inserted at regular intervals. These tufts are simple to remove. Single yarns typically make up flock/flake yarns.
Textured yarn:
These are constructed from fully drawn filament fibres that have been modified by novel spinning procedures to change their surface, form, and texture. Two of the most prevalent textured fibres are nylon and polyester. Textured yarns offer a wide range of fabric property variations. The two primary categories of textured yarns are:
1. Stretch yarns
2. Bulk yarns
Stretch yarn:
It is manufactured by using one of the following methods.
Stretch yarns are frequently continuous-filament man-made yarns that are very tightly twisted producing a spiral crimp giving a springy character.
Bulk Yarns:

When compared to tightly twisted yarns, bulk yarns are softer and more malleable. Furthermore, bulk yarns provide a better cover. They come in two varieties and produce less transparent fabrics:
1. High bulk yarns
2. Loop-bulk or air-jet yarns
